GAS : GNU assembler
NASM(Intel syntax) vs GAS(AT&T syntax)
ELF system
GNU assembler
NASM tutorial
Another NASM tutorial
X86 calling convention
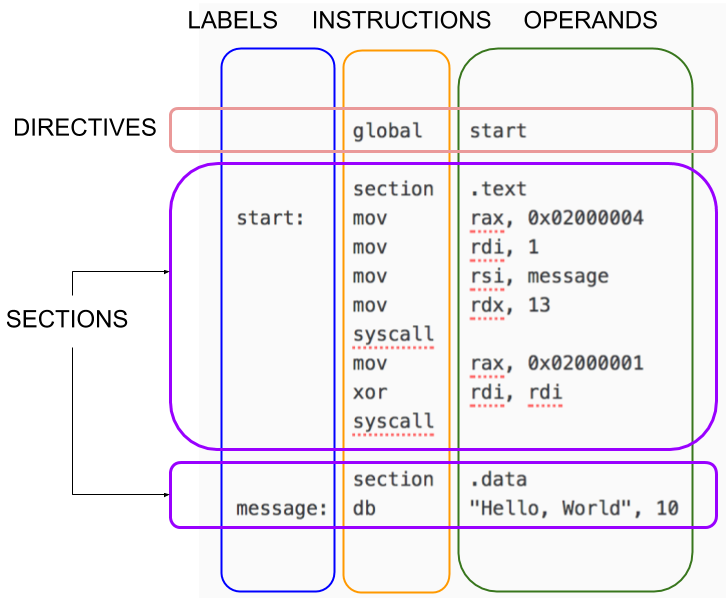
1 structure of a NASM program
2 寄存器
整形寄存器
64bits
R0 R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 R8 R9 R10 R11 R12 R13 R14 R15RAX RCX RDX RBX RSP RBP RSI RDI32bits
R0D R1D R2D R3D R4D R5D R6D R7D R8D R9D R10D R11D R12D R13D R14D R15DEAX ECX EDX EBX ESP EBP ESI EDI16bits
R0W R1W R2W R3W R4W R5W R6W R7W R8W R9W R10W R11W R12W R13W R14W R15WAX CX DX BX SP BP SI DI8bits
R0B R1B R2B R3B R4B R5B R6B R7B R8B R9B R10B R11B R12B R13B R14B R15BAL CL DL BL SPL BPL SIL DIL
浮点寄存器
16 XMM寄存器, 每一个寄存器128位宽度:
XMM0 … XMM15
3 内存寻址
1 | [number] |
[reg + reg scale + number] 完整版
reg为基址(base)
number为偏移(displacement)
reg scale是索引(index)
4 立即数
10进制
200
200d
0d20016进制
0c8h
0xc88进制
210q
0q2102进制
11001000b
0b1100_1000
5 运算指令
mul乘法指令
格式mul [操作数]
乘法指令的第一个操作数一定要放在eax寄存器之间,第二个操作数可以放在其他寄存器之中,运算结果存在eax寄存器中
7 调用约定
参数传递
从左到右,传递尽可能多的参数到寄存器中
整形 rdi rsi rdx rcx r8 r9
浮点 xmm0 xmm1 xmm2 xmm3 xmm4 xmm5 xmm6 xmm7
多余的参数以从右往左的顺序推入堆栈
返回地址 [rsp]
第一个参数[rsp + 8]
rsp对齐
The stack pointer rsp must be aligned to a 16-byte boundary before making a call. Fine, but the process of making a call pushes the return address (8 bytes) on the stack, so when a function gets control, rsp is not aligned. You have to make that extra space yourself, by pushing something or subtracting 8 from rsp.
清理
caller clean up
callee save
rbp rbx r12 r13 r14 r15
8 section
- data
text
bss
- undefined section
9 entry point
NASM默认入口是_start1
2
3GLOBAL _start
section text
_start:
可以用ld -o out a.o -e _main改变入口函数
what-is-global-start-in-assembly-language
10 使用syscall
- 将调用的syscall号码放在eax寄存器中
- 将参数按照顺序传入ebx ecx, etc
- 发出中断
- 结果在eax中
1 | section .text |
使用c库函数1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20section .text
global main
extern printf
main:
push rbp;
mov rbp, rsp;
sub rsp, 16;
mov dword [rbp - 16], 2;
movsx rax, dword [rbp - 16];
mov rdi, message;
mov rsi, rax;
call printf;
add rsp, 16;
mov eax, 0;
pop rbp;
ret;
section .data
message db "Register = %0d", 10, 0
11 mov
mov指令无法在memory和memory之间移动
需要加入寄存器作为中介
不是16字节对齐会引起segment fault
12 fpu
fpu register
13 type specifier
mov指令用于
- 两个寄存器之间 (移动内容确定 因为寄存器大小确定)
寄存器和内存地址之间 (移动内容不确定 因为内存地址指向的大小不定)
如果不用type specifier, 移动内容大小为寄存器大小1
2mov eax, [ebp - 4]; 4 bytes
movsx eax, WORD [ebp - 4]; 2 bytes, signed extended寄存器和立即数 (移动内容不确定 因为立即数大小不确定)
- 内存地址和立即数 (移动内容不确定 因为内存地址指向的大小和立即数大小不定)
14 named memory
db (define byte) 声明byte大小的内存
dd (define double word) 声明double word大小的内存
dw (define word) 声明word大小的内存1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21section .text
global main
extern printf
main:
push rbp;
mov rbp, rsp;
sub rsp, 16;
mov dword [rbp - 16], 2;
movsx rax, dword [rbp - 16];
mov rbx, 2;
mov rdi, message + 14;
mov rsi, rax;
call printf;
add rsp, 16;
mov eax, 0;
pop rbp;
ret;
section .data
message db "Register = %0d","Register = %0d", 10, 0